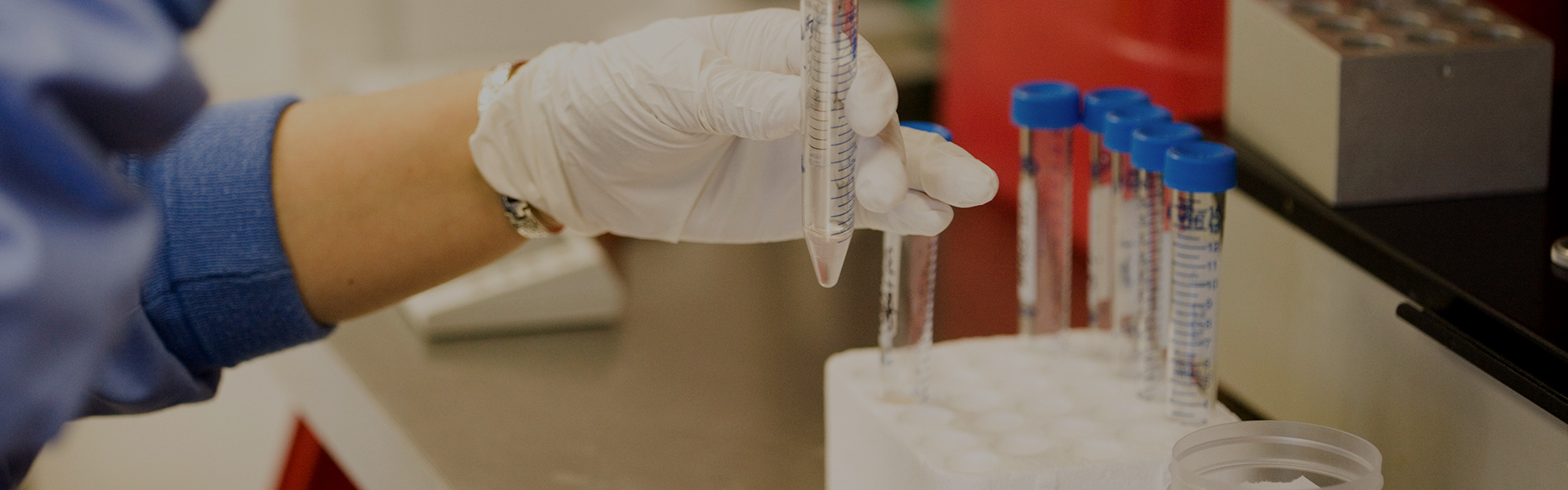
주요연혁 / 연구실적
연구활동 Effects of phosphate, energy substrates, and amino acids on developmen…
페이지 정보
Effects of phosphate, energy substrates, and amino acids on development of in vitro-matured, in vitro-fertilized bovine oocytes in a chemically defined, protein-free culture medium Jong-Heung KIm, Koji NIWA, Jeong-Mook LIM, Kiyoshi OKUDA
Biology of Reproduction 48:1320-1325, 1993
Effects of phosphate, energy substrates, and amino acids on development
of in vitro-matured, in vitro-fertilized bovine oocytes in a chemically
defined,protein-free culture medium
JH Kim, K Niwa, JM Lim and K Okuda
Division of Animal Science and Technology, Faculty of Agriculture,
Okayama University, Okayama 700, Japan.
Abstract
Bovine oocytes that had been matured and fertilized in vitro were cultured
in a simple, chemically defined, protein-free medium (mTLP- PVA). When the
medium was supplemented with 19 amino acids, development to the 8-cell (14-
20% vs. 38-46%), morula (0-6% vs. 27-32%), and blastocyst (0-1% vs. 9-13%)
stages 96, 144, and 192 h after insemination, respectively, was
significantly greater in the absence than in the presence of glucose (5.56
mM) regardless of the presence of phosphate (1.05 mM). However, blastocyst
development was difficult in medium with any combination of glucose and
phosphate without amino acids. In mTLP-PVA with amino acids and different
concentrations of phosphate, the highest proportions of embryos reaching
the > or = 8- cell (56%), morula (44%), and blastocyst (24%) stages were
obtained at a 0.35 mM concentration. When lactate and pyruvate were
omitted from mTLP-PVA (mT-PVA) supplemented with amino acids and 0.35 mM
phosphate, the first cleavage was completely inhibited. Although lactate
or pyruvate alone could support blastocyst development to a limited extent
(10-15%), a significantly higher proportion (22%) of blastocysts was
obtained in medium with both lactate (10 mM) and pyruvate (0.5 mM).